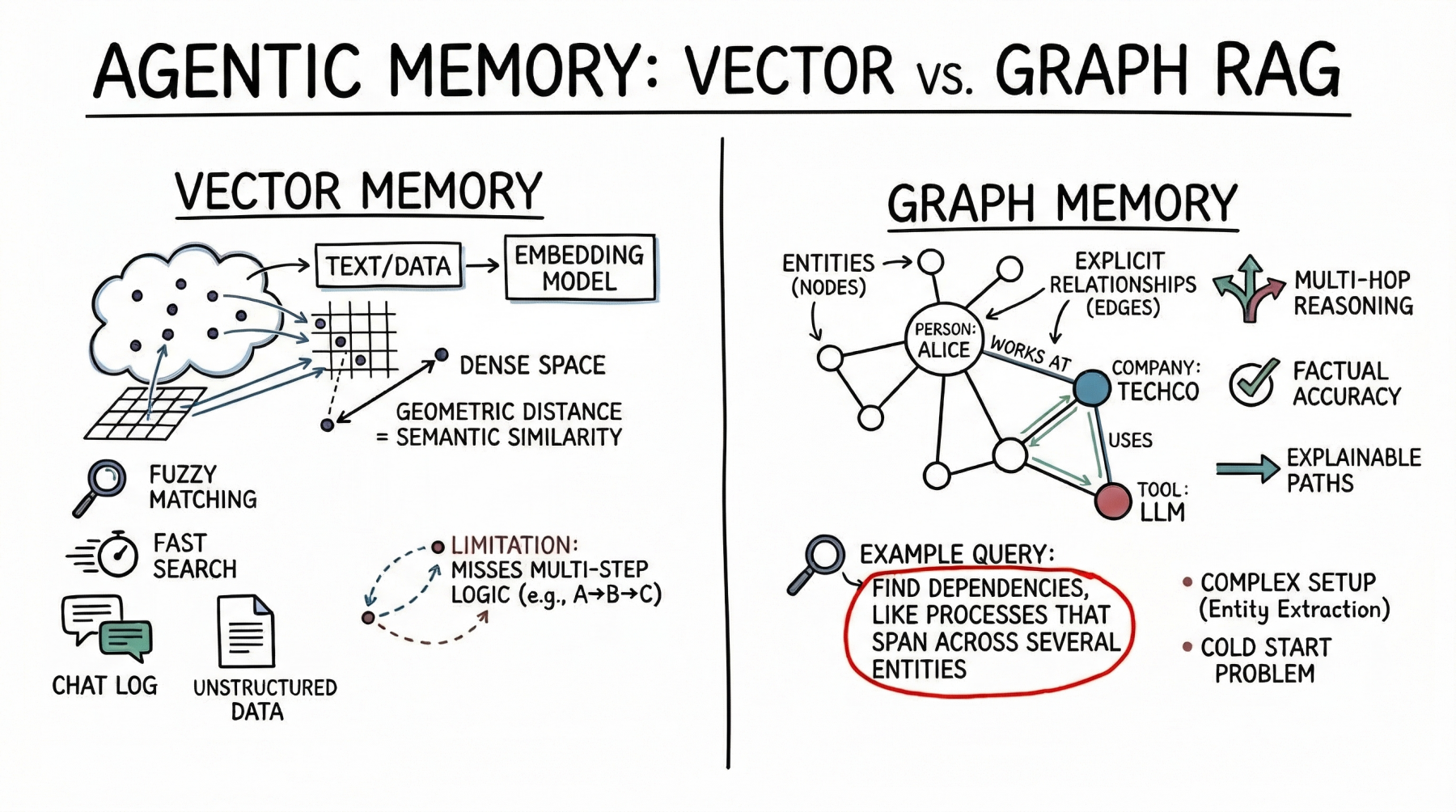
Vector Databases vs. Graph RAG for Agent Memory: When to Use Which
<a href="https://machinelearningmastery.

<a href="https://machinelearningmastery.
<a href="https://machinelearningmastery.
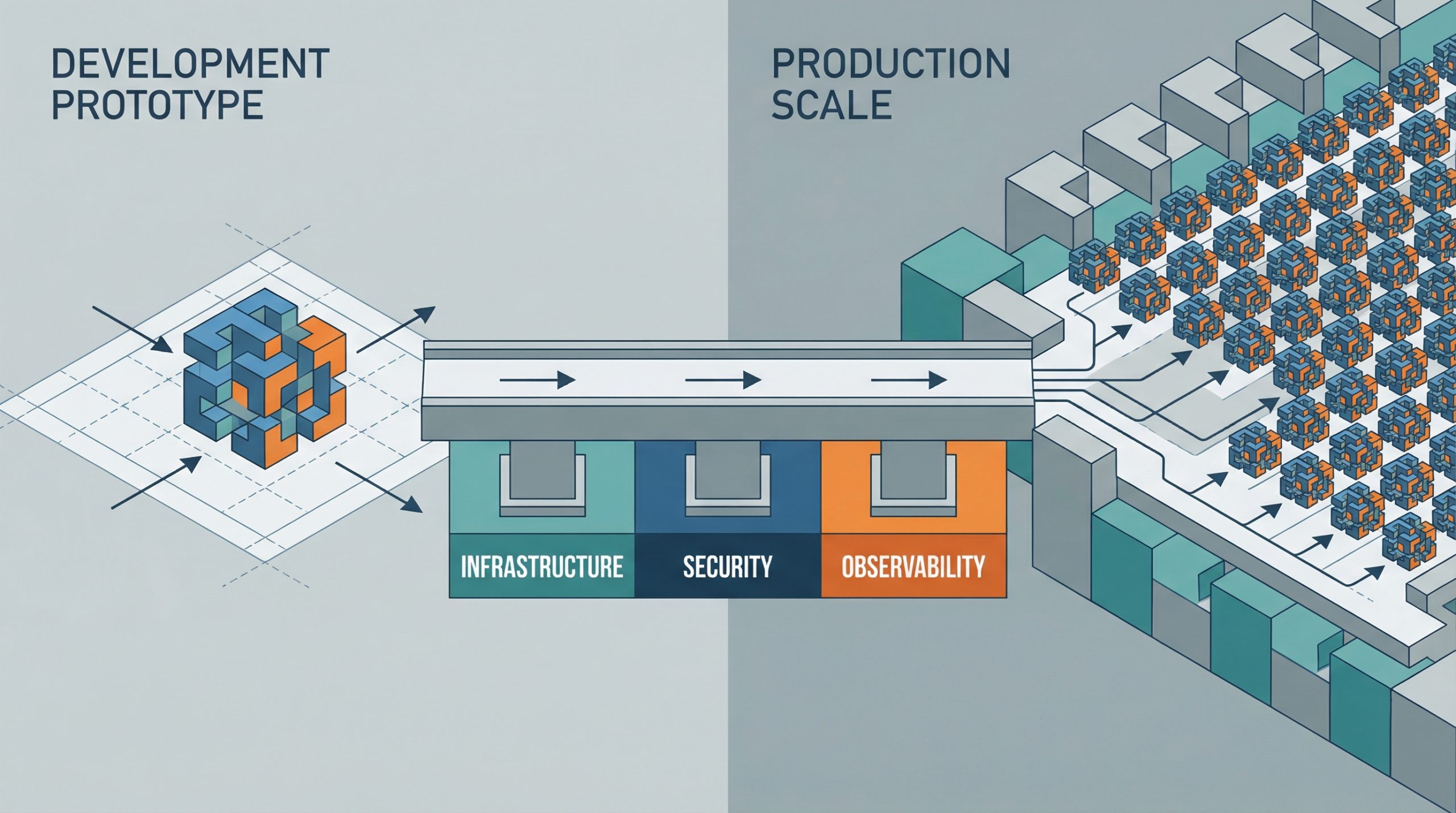
You've built an AI agent that works well in development.
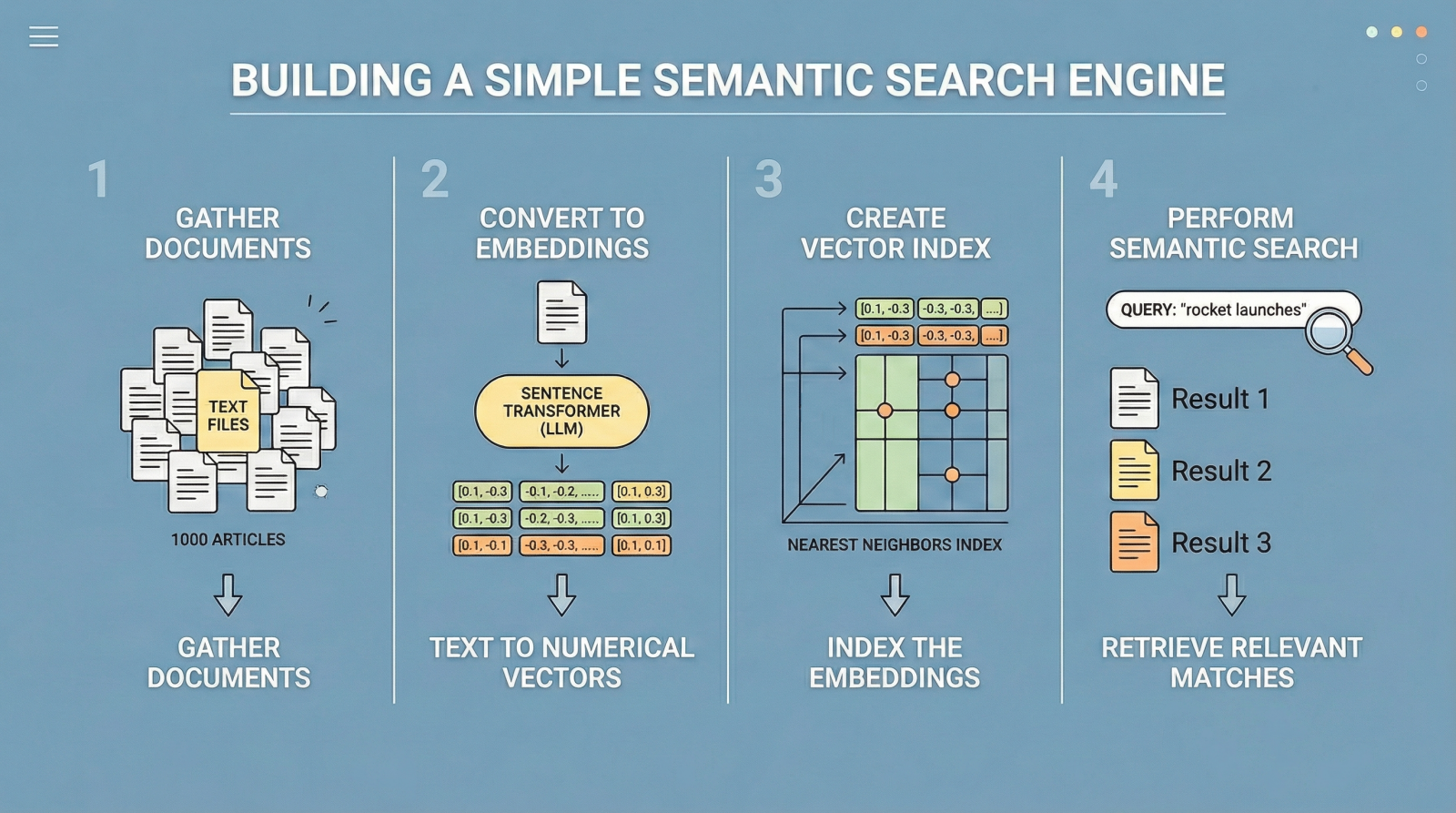
Traditional search engines have historically relied on keyword search.
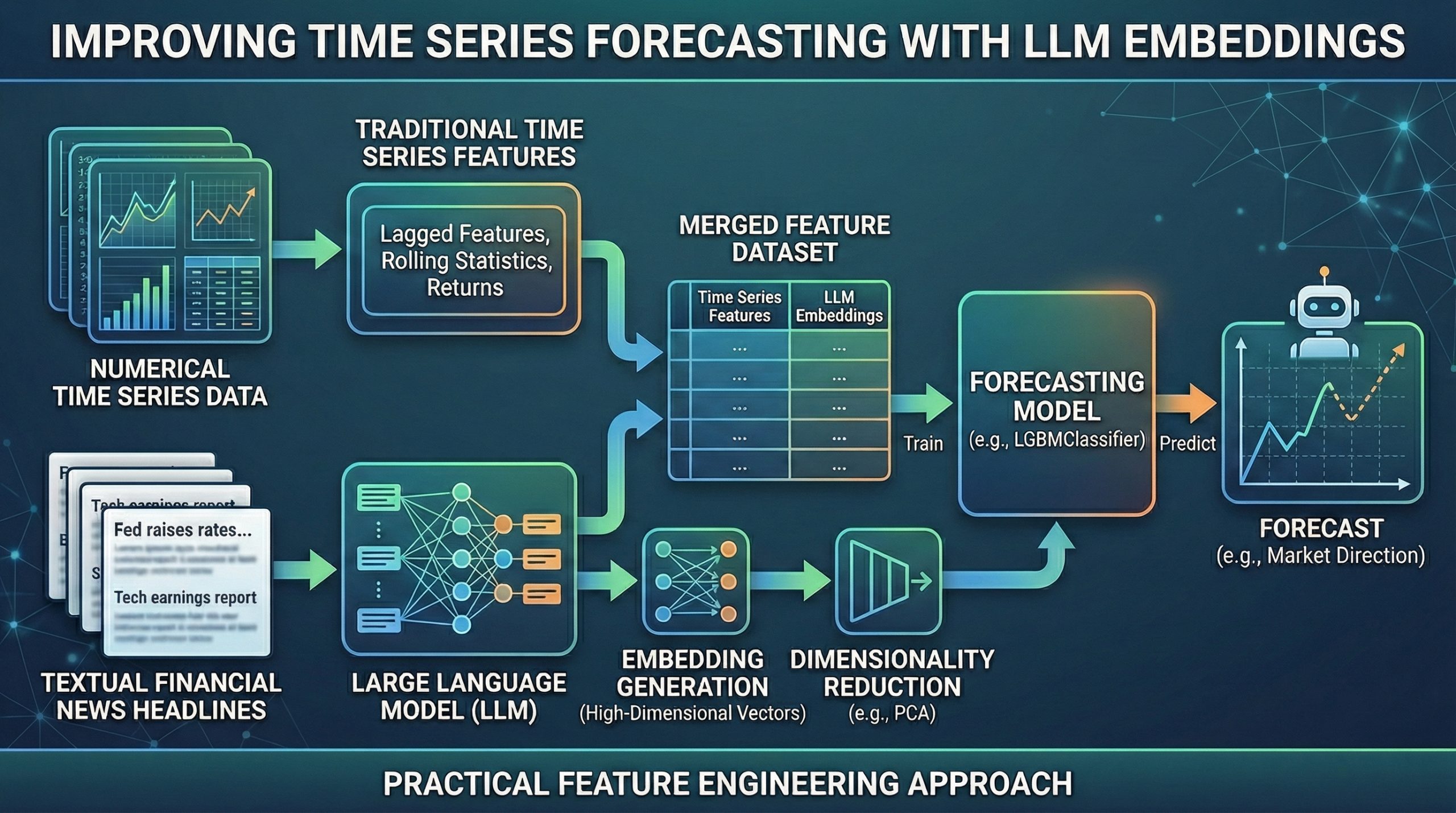
Using large language models (LLMs) — or their outputs, for that matter — for all kinds of machine learning-driven tasks, including predictive ones that were already being solved long before language models emerged, has become something of a trend.
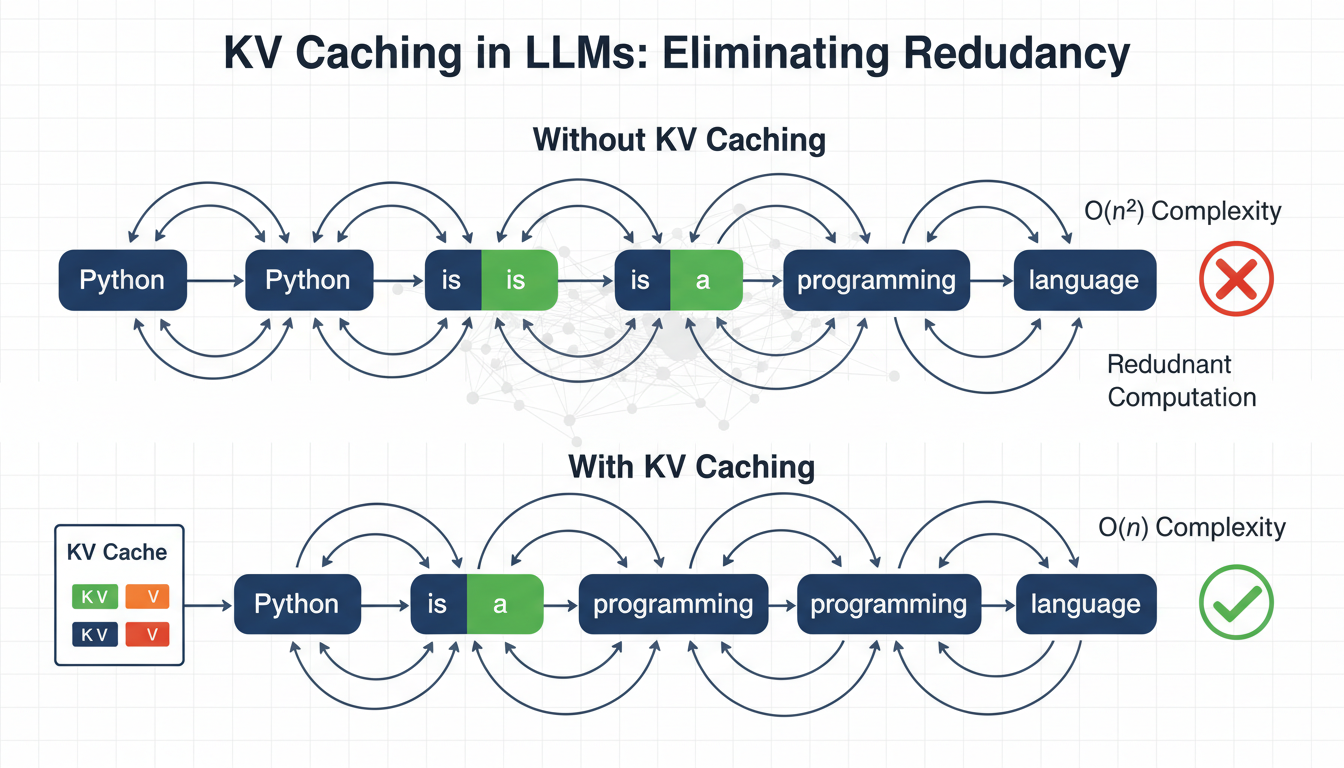
Language models generate text one token at a time, reprocessing the entire sequence at each step.
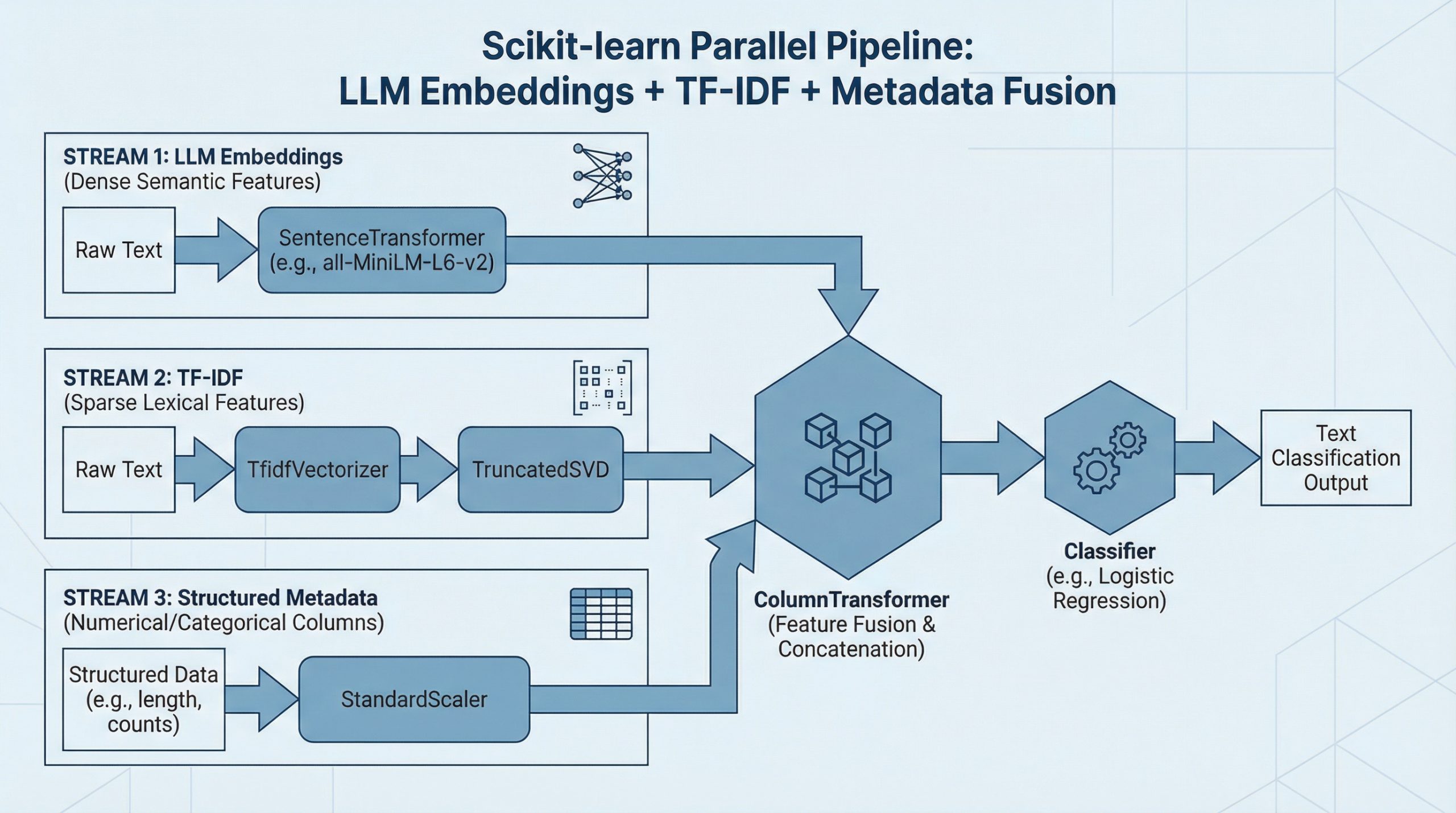
Data fusion , or combining diverse pieces of data into a single pipeline, sounds ambitious enough.
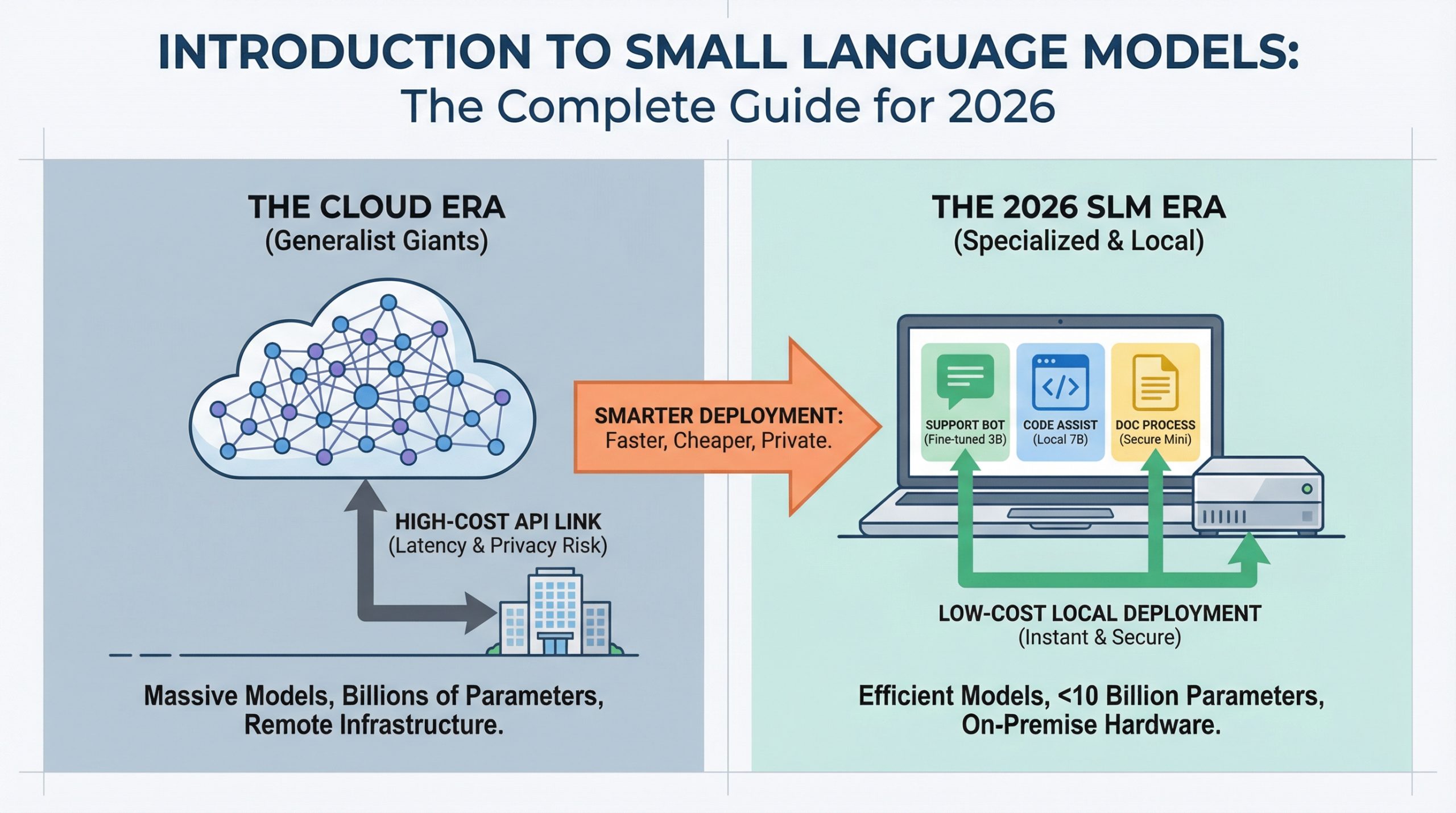
AI deployment is changing.
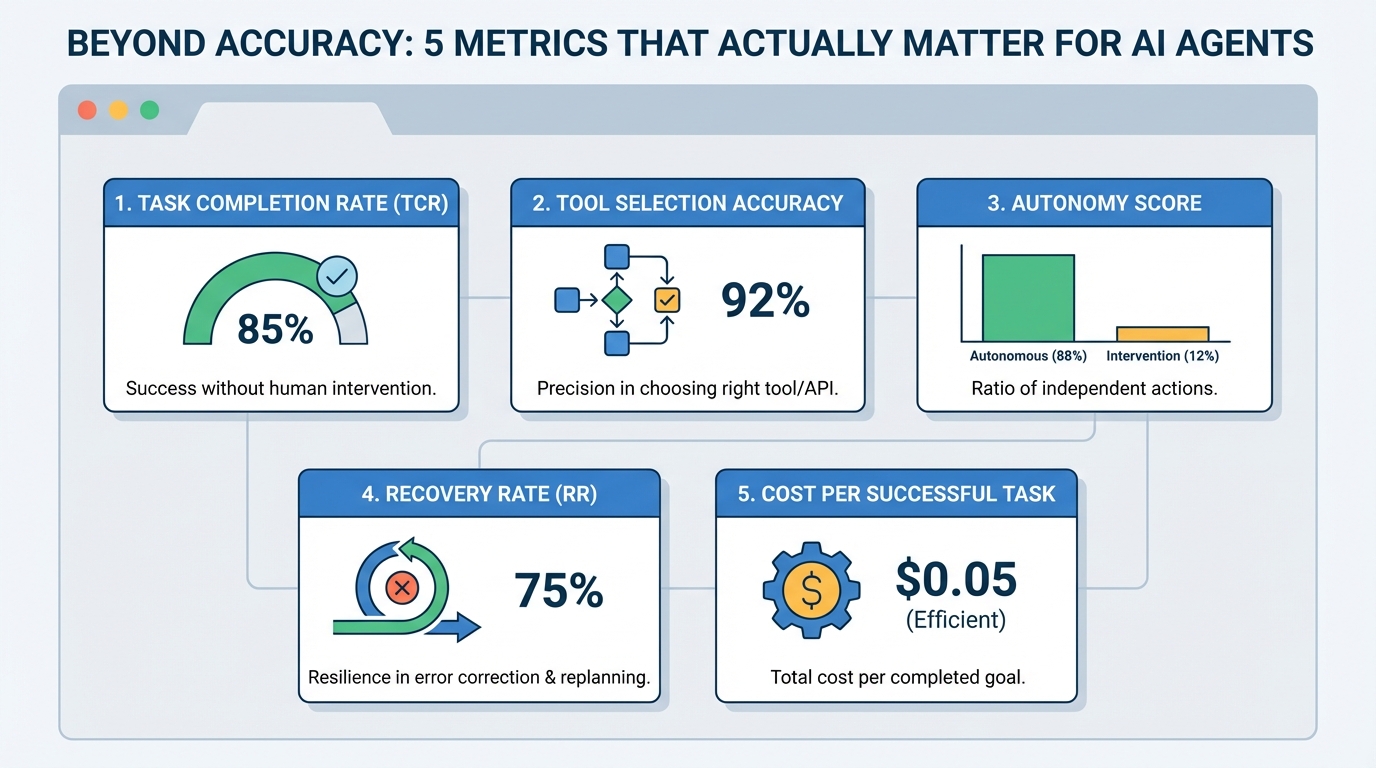
AI agents , or autonomous systems powered by agentic AI, have reshaped the current landscape of AI systems and deployments.
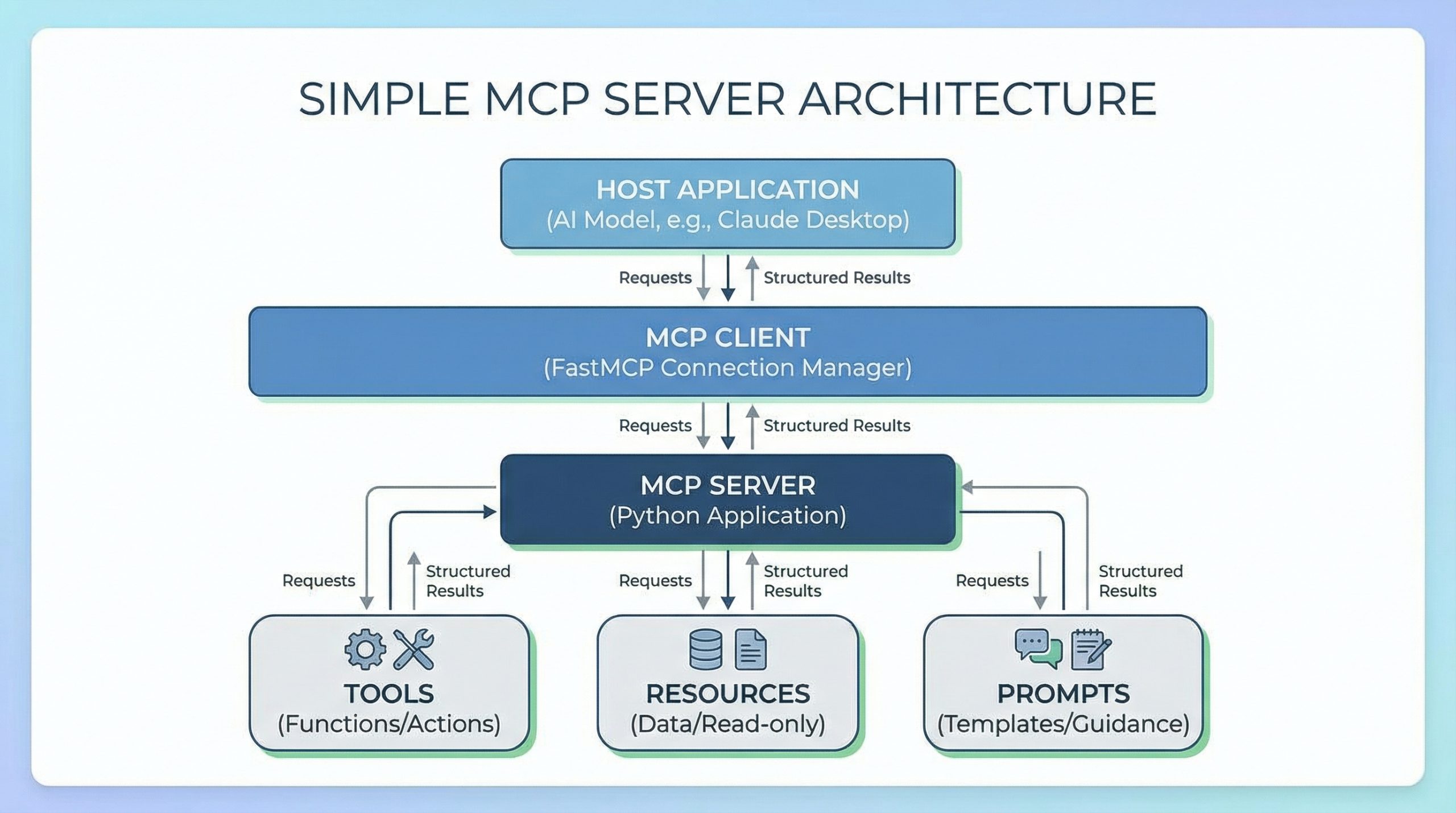
Have you ever tried connecting a language model to your own data or tools? If so, you know it often means writing custom integrations, managing API schemas, and wrestling with authentication.
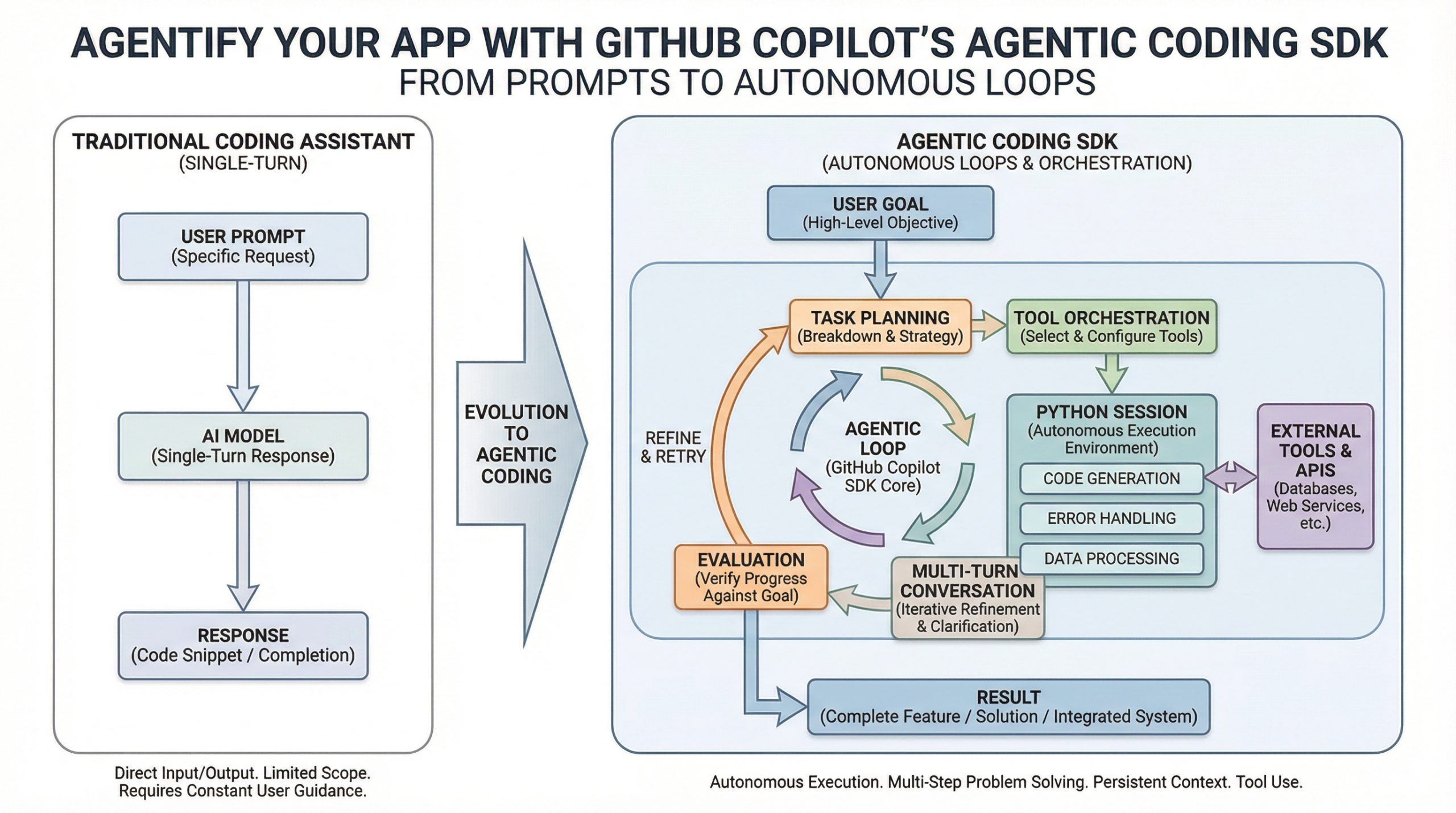
For years, GitHub Copilot has served as a powerful pair programming tool for programmers, suggesting the next line of code.
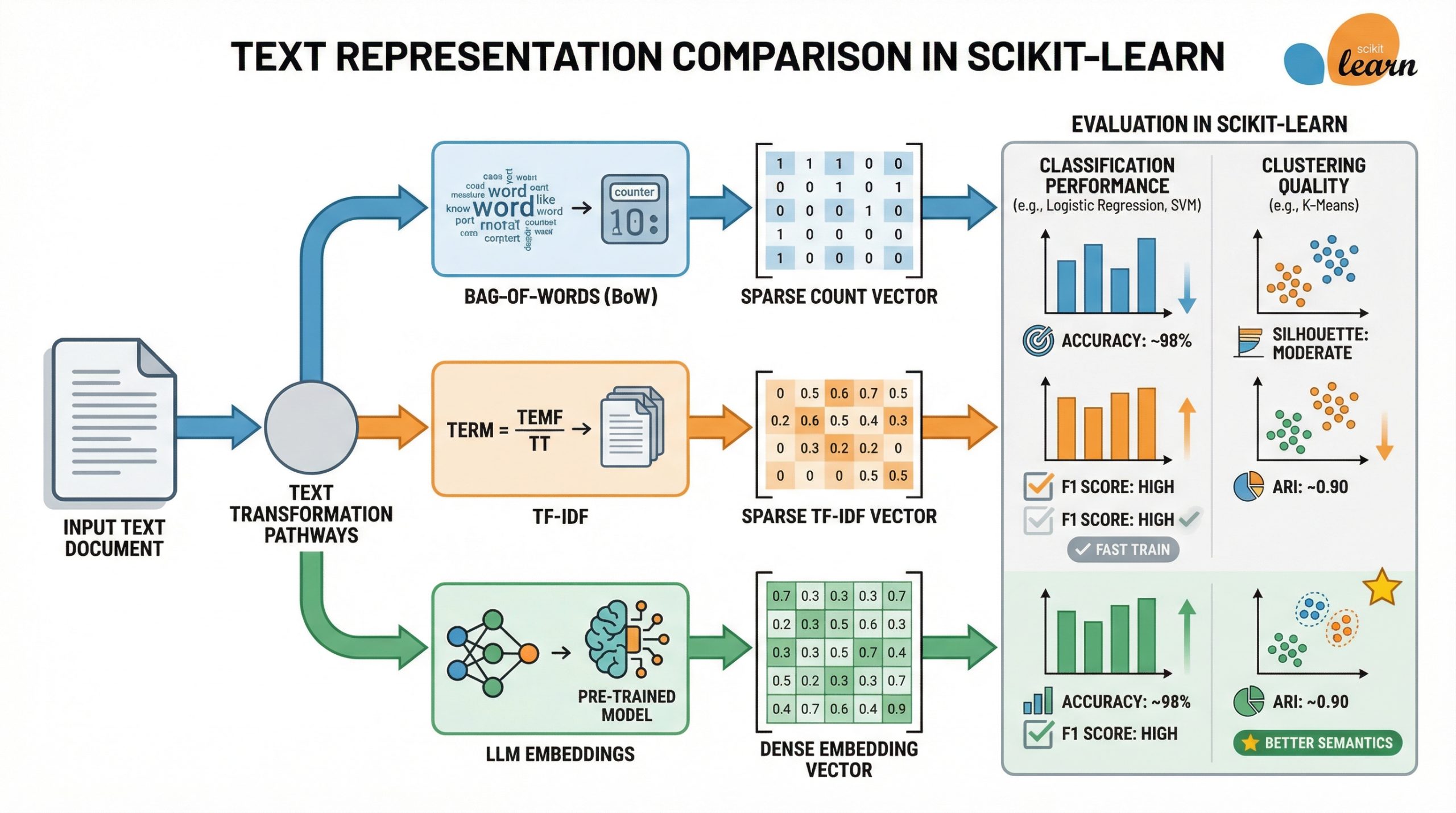
Machine learning models built with frameworks like scikit-learn can accommodate unstructured data like text, as long as this raw text is converted into a numerical representation that is understandable by algorithms, models, and machines in a broader sense.
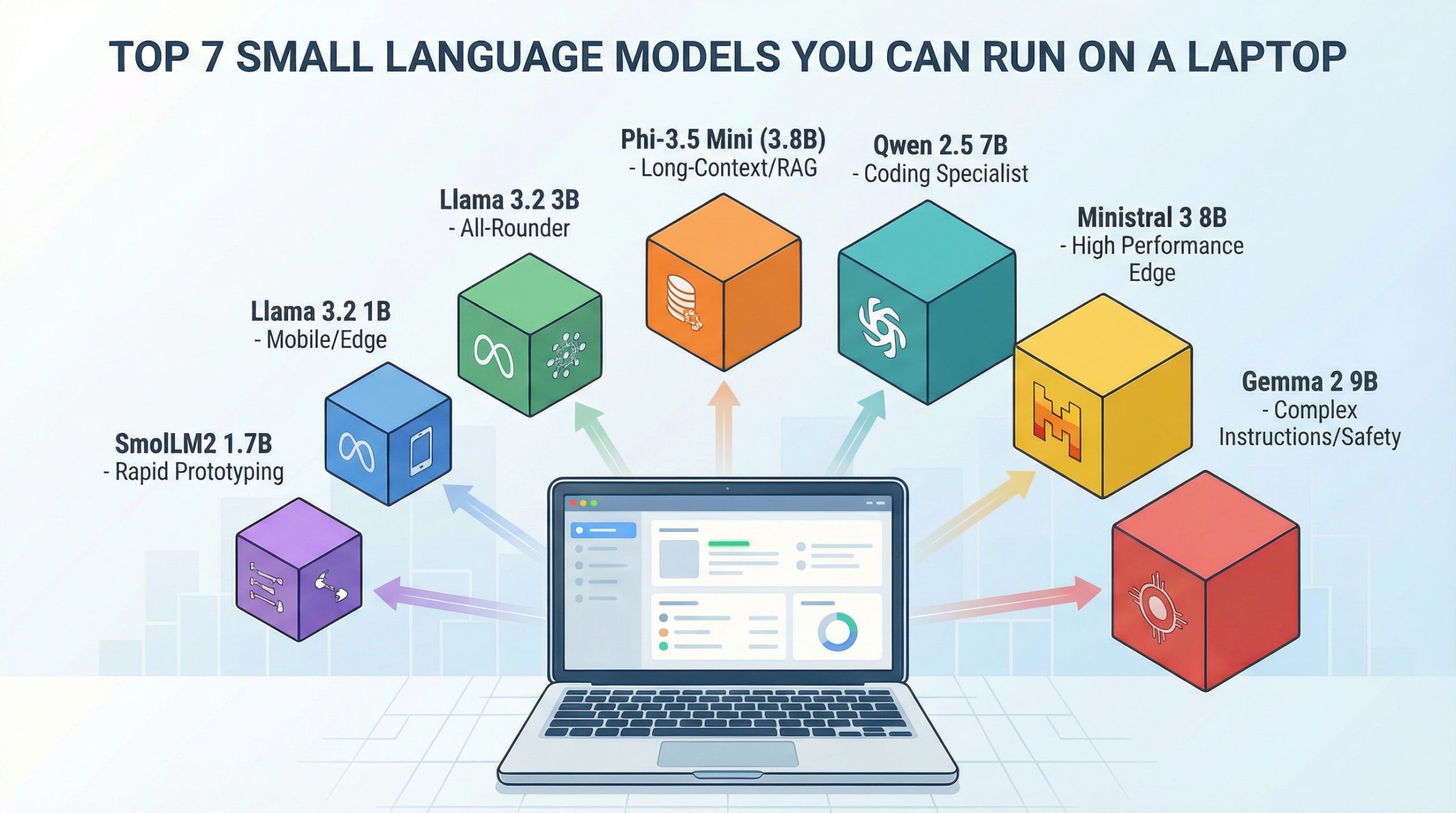
Powerful AI now runs on consumer hardware.
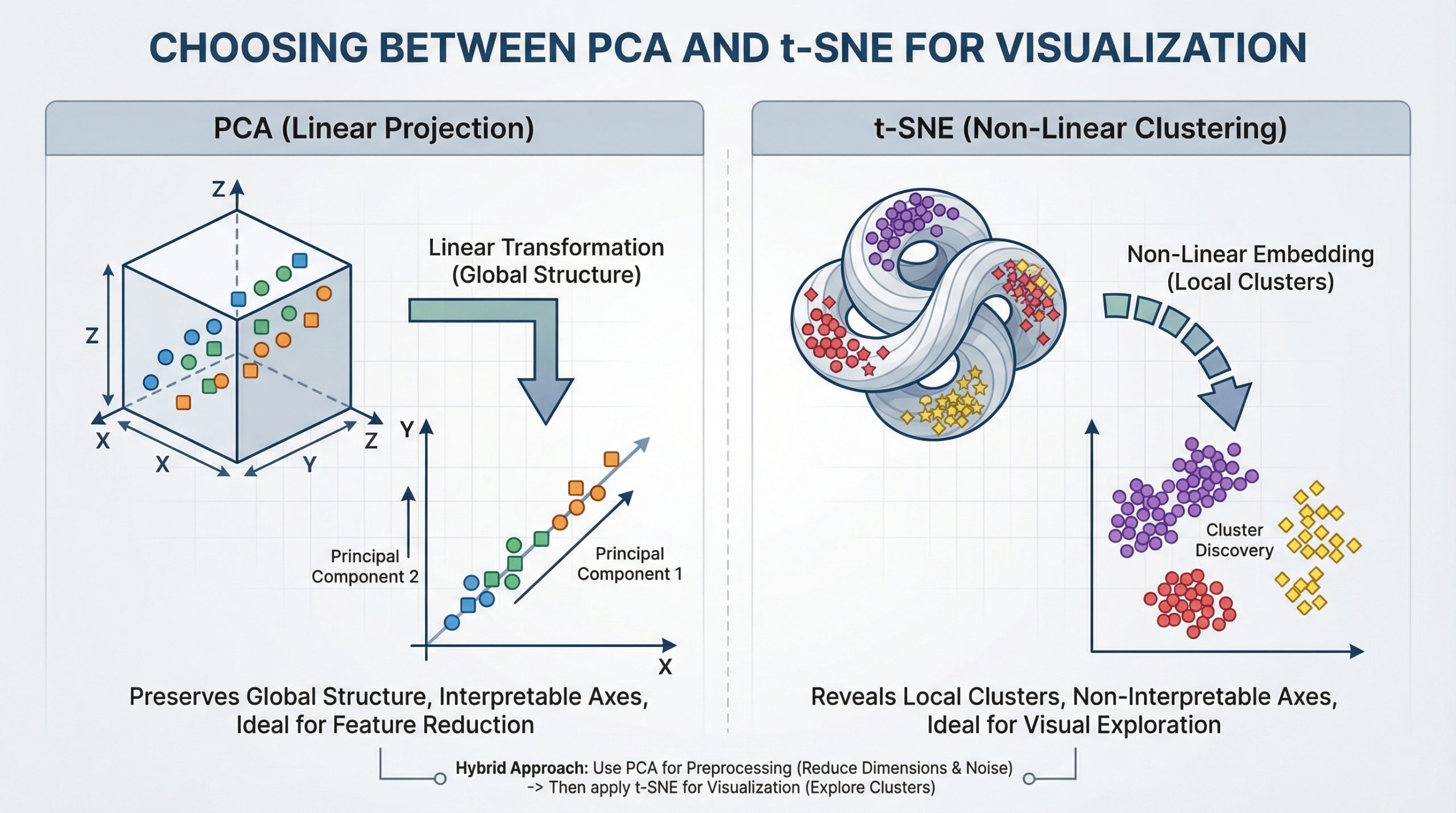
For data scientists, working with high-dimensional data is part of daily life.

When building machine learning models, training is only half the journey.
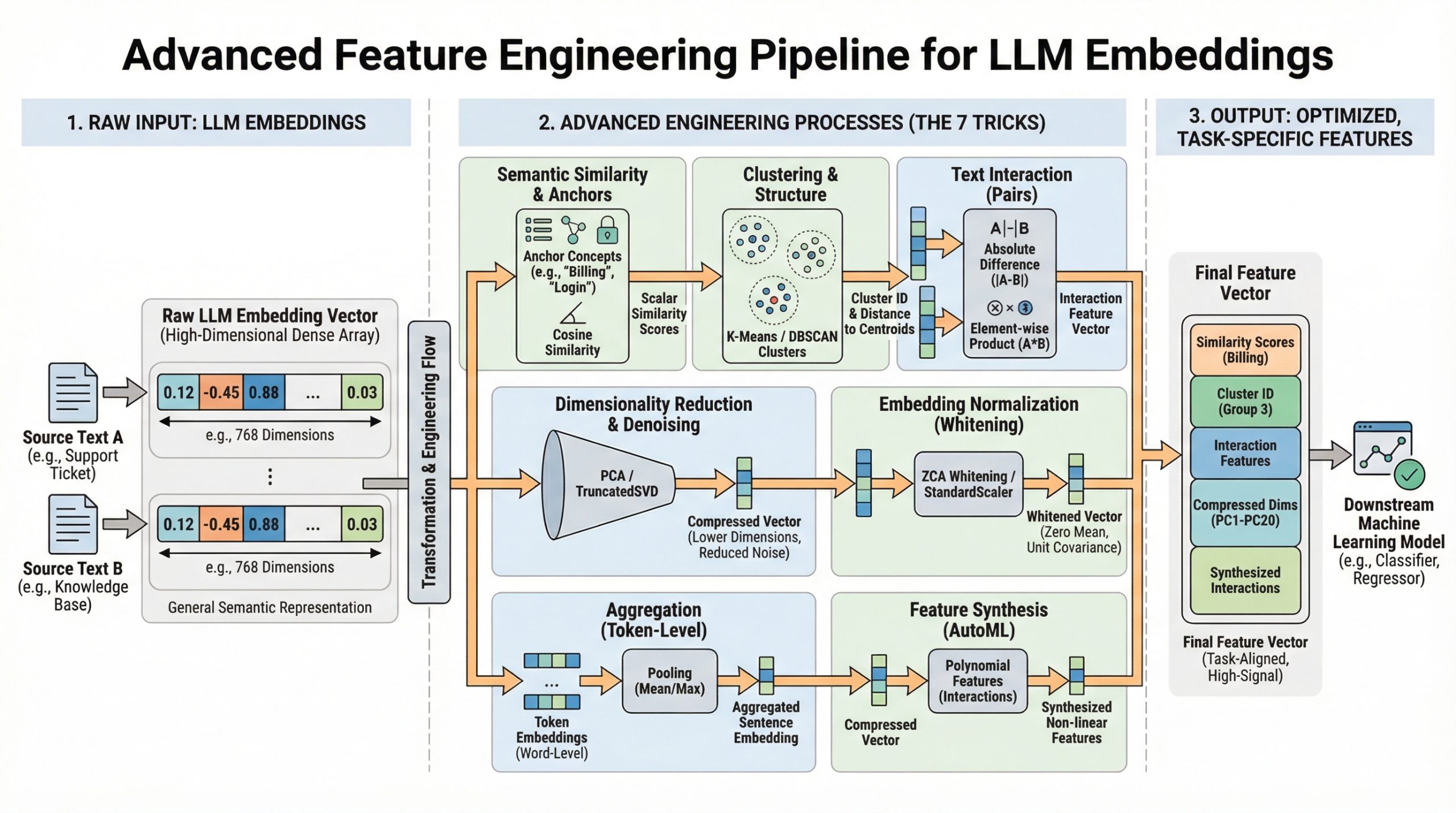
You have mastered model.
The large language models (LLMs) hype wave shows no sign of fading anytime soon: after all, LLMs keep reinventing themselves at a rapid pace and transforming the industry as a whole.

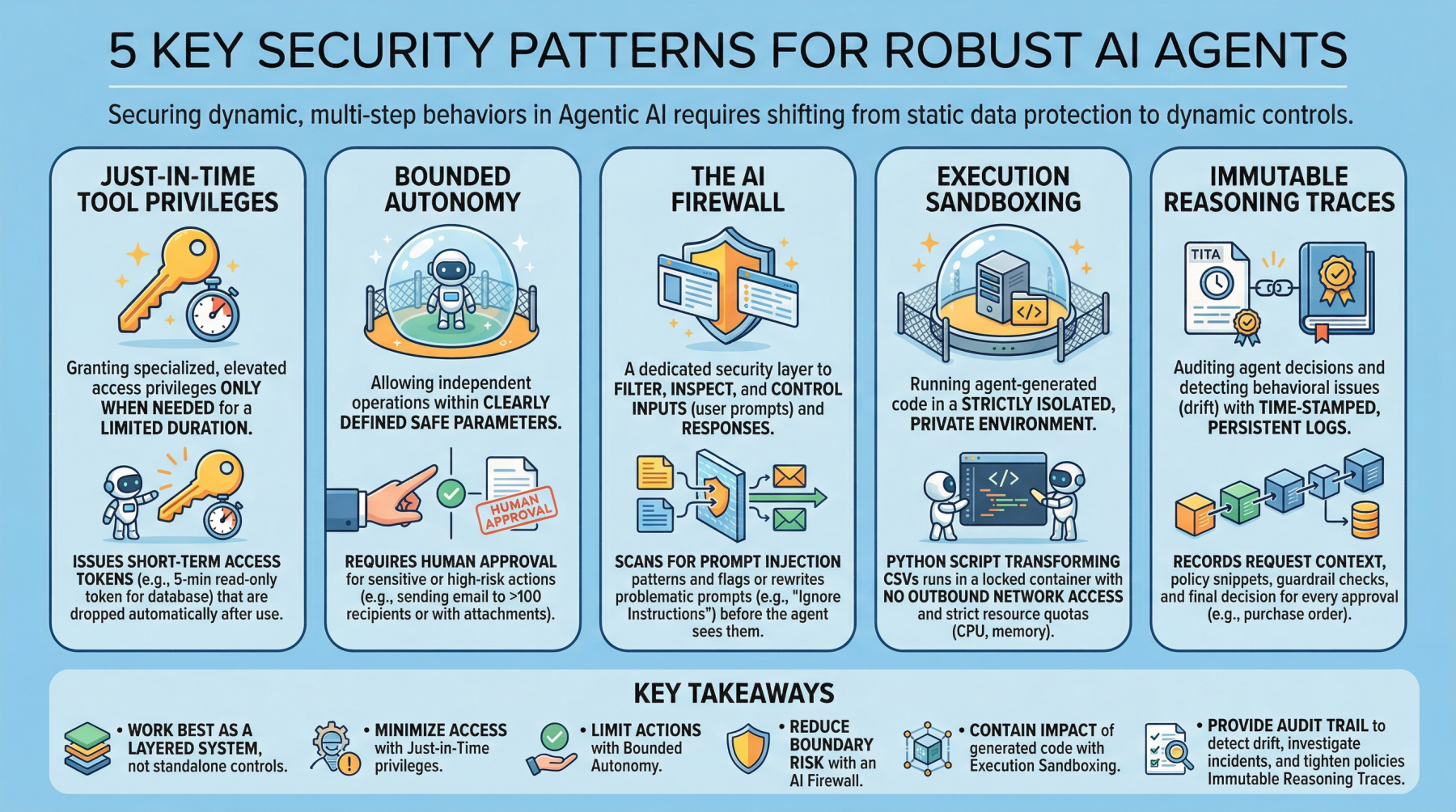
The promise of agentic AI is compelling: autonomous systems that reason, plan, and execute complex tasks with minimal human intervention.
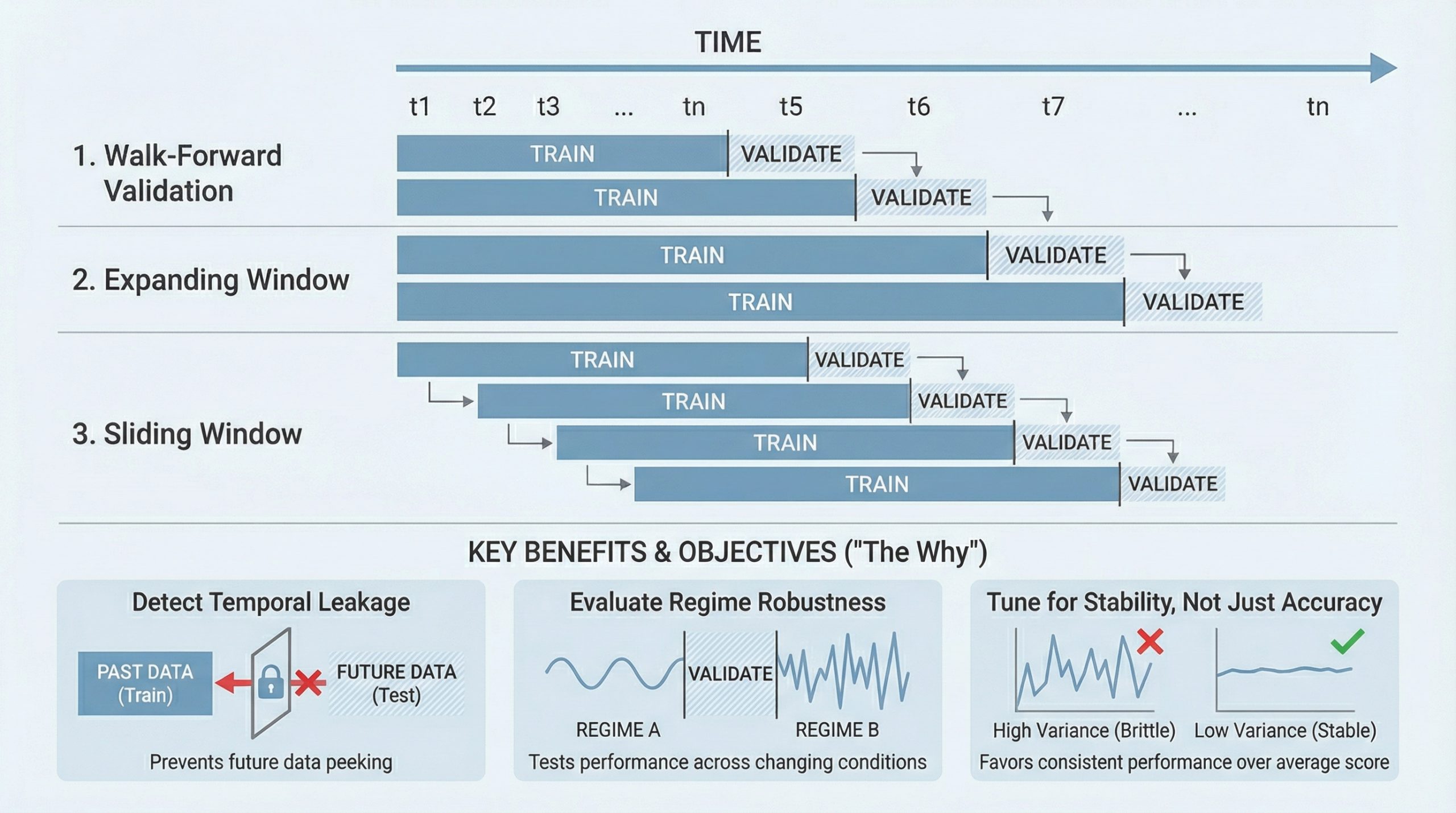
Time series modeling <a href="https://machinelearningmastery.
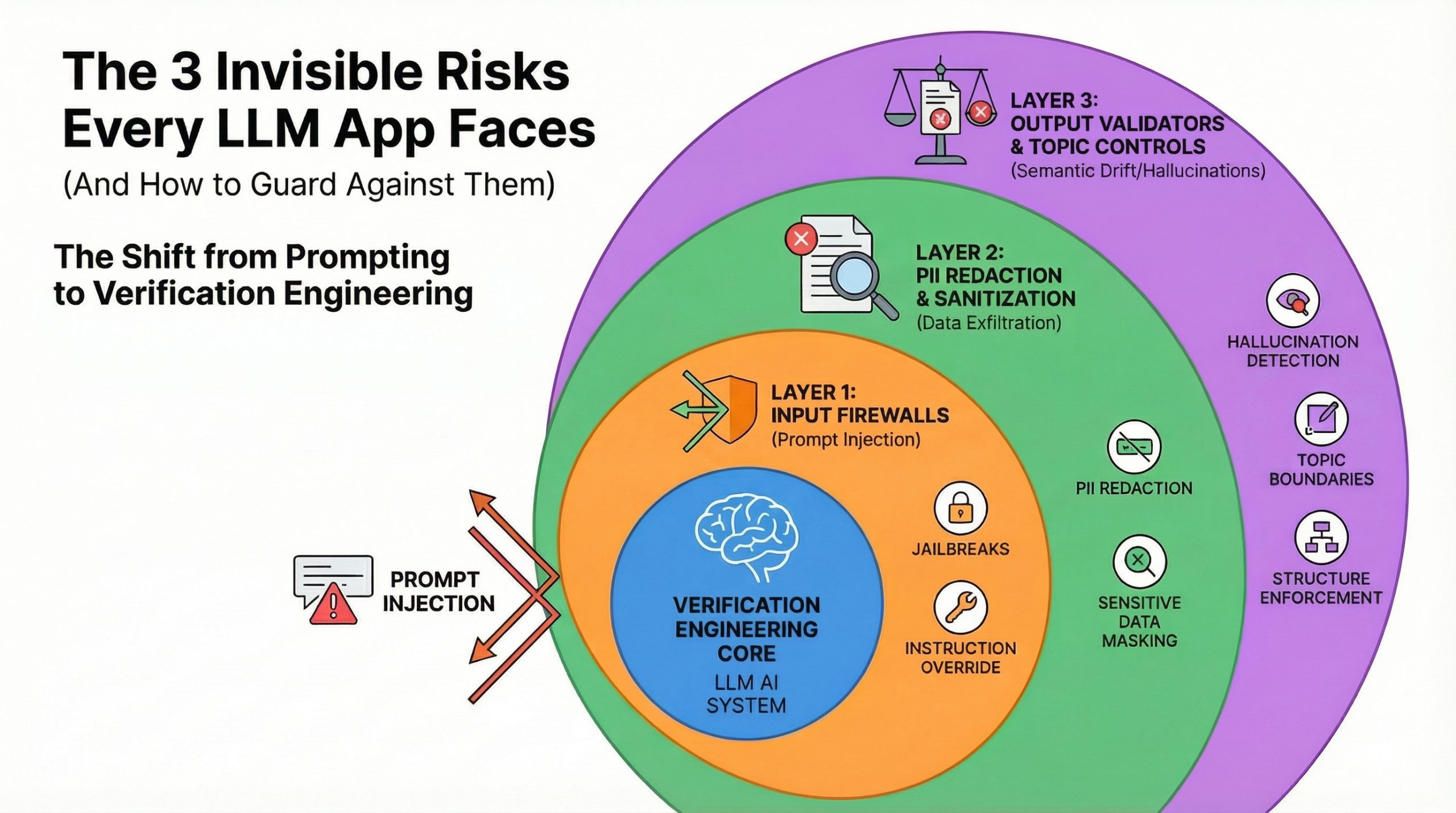
Building a chatbot prototype takes hours.